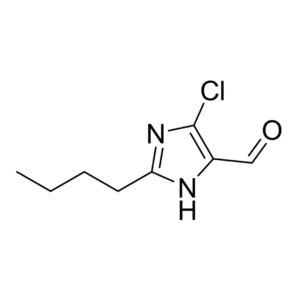
The intricate dance of our bodies’ functions rests heavily on the balance of nutrients we consume. One significant player in this balance is Benfotiamine, a synthetic sibling of thiamine, more commonly known as Vitamin B1. This extended discussion on Benfotiamine will explore its origin, structure, functions, therapeutic benefits, and potential risks.
ORIGINS AND STRUCTURAL CHARACTERISTICS
Benfotiamine, a fat-soluble thiamine derivative, has a distinct advantage over its water-soluble counterpart: it exhibits improved bioavailability. Simply put, when you ingest Benfotiamine, your body is more adept at absorbing and utilizing it than standard thiamine.
DIFFERENCES FROM THIAMINE
While Benfotiamine is structurally different from thiamine, its primary function is to elevate the blood and tissue concentrations of thiamine and thiamine phosphate esters. This enhanced bioavailability is what makes it a favored choice in several therapeutic applications.
THE WORKING MECHANISM: FROM INTAKE TO ACTION
Understanding how Benfotiamine functions is key to grasping its significance. Once ingested, the body metabolizes it back to thiamine. Thiamine, then, plays a pivotal role in glucose metabolism, acting as an essential coenzyme in our cells’ energy production process. By amplifying the body’s thiamine levels, Benfotiamine assists in promoting glucose metabolism, mitigating oxidative stress, and potentially reducing the complications associated with conditions like diabetes.
THERAPEUTIC EXPLOITS: WHERE BENFOTIAMINE SHINES
Benfotiamine’s therapeutic versatility is commendable. Let’s delve deeper into some of its primary applications.
1. NEUROPATHY AND NERVE HEALTH
Benfotiamine is prominently recognized for its role in managing peripheral neuropathy, notably diabetic neuropathy. Patients with this condition often experience nerve damage in the hands and feet, leading to symptoms such as pain and numbness. By augmenting thiamine levels and bolstering glucose metabolism, Benfotiamine can alleviate some of these distressing symptoms.
2. ALLEVIATING ALCOHOL WITHDRAWAL SYMPTOMS
Chronic alcohol consumption can severely deplete thiamine levels, laying the foundation for disorders like Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Given Benfotiamine’s high bioavailability, it is a preferred agent in preventing and treating thiamine deficiency during alcohol withdrawal.
3. HEART AND KIDNEY HEALTH
There’s growing evidence suggesting Benfotiamine’s benefits extend to heart and kidney health, especially among diabetic individuals. By reducing advanced glycation end products (AGEs) that intensify diabetic complications, Benfotiamine offers a promising route for enhanced cardiac and renal function.
4. EMERGING THERAPEUTIC AVENUES
Recent research avenues are exploring the potential role of Benfotiamine in age-related cognitive decline and conditions such as Alzheimer’s. While concrete conclusions are still on the horizon, these research trajectories hold immense promise.
POTENTIAL ADVERSITIES: SIDE EFFECTS AND CONCERNS
No therapeutic agent is devoid of side effects, and Benfotiamine is no exception.
1. DIGESTIVE DISCOMFORTS
Some users might experience gastrointestinal disturbances, including nausea or stomach pain. These side effects typically wane as the body acclimatizes to the supplement.
2. ALLERGIC MANIFESTATIONS
Although uncommon, allergic reactions to Benfotiamine can occur. It’s imperative to seek immediate medical intervention if symptoms like severe itching, dizziness, or respiratory difficulties arise.
3. DRUG INTERACTIONS
Before commencing Benfotiamine, a thorough discussion with your healthcare provider about all other medications and supplements you’re taking is crucial. This pre-emptive measure helps in averting potential adverse drug interactions.
ESSENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS: PRECAUTIONS TO HEED
1. Medical Conditions: Individuals diagnosed with specific medical conditions, particularly certain types of cancers, should proceed with caution. Elevated thiamine levels might potentially accelerate tumor growth, so a consultation with a healthcare professional is paramount.
2. Pregnancy and Lactation: As with most supplements, pregnant and lactating women should consult their healthcare provider before initiating Benfotiamine to ensure safety for both mother and child.
3. Dosage Diligence: Adhering to the recommended dosage is pivotal. Overconsumption can lead to an array of complications, so always stick to prescribed or recommended amounts.
THE VERDICT: A POWERFUL ALLY WITH POTENTIAL
In the vast world of supplements, Benfotiamine holds a distinguished place. Its enhanced bioavailability and array of therapeutic applications make it an invaluable resource, especially in neuropathy management and thiamine deficiency scenarios.
As we traverse the health and wellness journey, understanding such agents and their nuanced roles in our bodies can empower us to make informed choices, ensuring that we tread on the path of robust health with informed steps.